GDPR Fines
Under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), for the first time in history, fines for privacy infringement in the EU could reach into the tens of millions of euros. Needless to say, noncompliance isn't worth it.
This article will break down the articles of the GDPR that deal with penalties of noncompliance. It will also provide some useful examples of GDPR violations that are easy to overlook but luckily also easy to resolve and remedy.
The General Data Protection Regulation In Short
The GDPR is a massive legal document, but here's an ultra-condensed summary of some of its most notable measures:
- No business in the EU or elsewhere may collect the personal information of an EU resident without first obtaining express, unambiguous, freely-given consent. This includes ambiguous data collected by browser cookies.
- EU users must be given easy access to their personal information in order to review, edit, or delete it. A full digital copy of a user's personal data must be provided upon request.
- The protection and security of personal data should be designed into the entire infrastructure of a website or mobile app. Privacy by Design is no longer a recommendation. It's a requirement.
- Privacy Policies should be written using clear, plain language and made accessible to users. In the same spirit of transparency, changes to privacy processing protocols and data breaches must be communicated to the users they affect in a timely manner.
Certain companies that process massive amounts of personal data, like social media networks and data processing firms, will need to follow many additional stipulations.
Who Will Be Affected?
Although the regulation will only apply to the personal data of EU residents, the GDPR will be enforced upon any business in the entire world that collects that information.
Since the internet is international by its very nature, there is no way to avoid compliance, at least as far as EU user data is concerned. Unless you can guarantee that no EU resident will ever come across your website/app, it would be in your best interest to comply. The EU is a major world power and most developed countries are prepared to cooperate with them to enforce the GDPR.
Penalties of Noncompliance
In order to manage the investigation and enforcement of the GDPR, a Data Protection Authority will be designated in each EU member state as the supervisory authority.
These supervisory authorities will be appointed by government officials in each member state and manage the day-to-day enforcement of the GDPR. You might think of them as the GDPR police.
EU consumers will have the option to submit privacy complaints directly to supervisory authorities. These will be the authorities you must report to in the case of a data breach of EU user information. They will exert full powers of the investigation and correction of GDPR infringement. In other words, they can dole out fines.
Under Article 58 Section 2 of the GDPR, supervisory authorities may take any of the following corrective actions in the case of EU consumer privacy infringement:

Fines
While most of the administrative corrections listed above are feasible and relatively simple for the affected businesses to comply with, it's the administrative fines that have online businesses the world over scrambling to meet GDPR requirements.
For the first time ever, fines for privacy violations could reach amounts of €20 million or more.
Article 83 deals with the general conditions for imposing administrative fines. Section 4 lists out what types of infringements come with a fine of up to €10 million or 2% of the company's global annual turnover, whichever is higher.

Section 5 of Article 83 outlines what infringements come with higher fines of up to €20 million or 4% of the company's global annual turnover, whichever is higher.

Section 2 of Article 83 provides a list of criteria for the supervisory authorities to consider when determining the amount of the fine to be imposed:
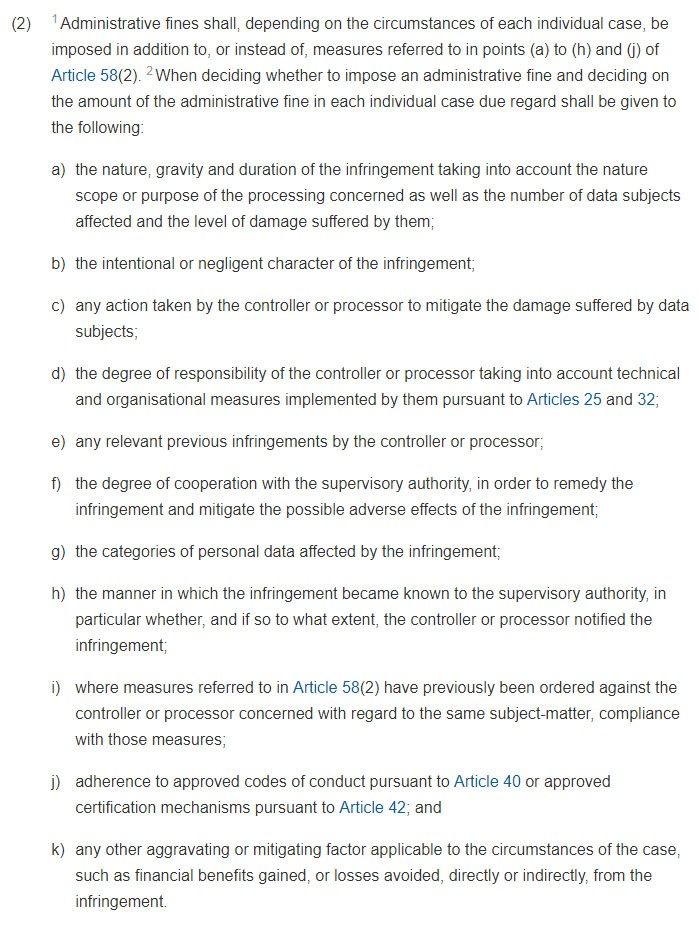
As you can see, a variety of factors will affect each individual case including aggravating and mitigating factors, how negligent or intentional the violation was, past violations, etc.
It is important to note that fines and penalties are supposed be fair and appropriate to each individual infraction. If your violation of the GDPR is an honest mistake and you make fair efforts to mitigate it, your fines will not be towards the top of the spectrum.