Impact of GDPR
If your business collects, stores, processes or shares personal user data, it must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The European Union (EU) established this law in 2018 as a response to citizen concerns about privacy and data protection. The GDPR provides a single set of data protection laws for the entire EU while giving users more control over their personal data.
What Is the GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a law regulating personal data use for individuals who live in the EU and the European Economic Area (EEA). The GDPR replaced the previous Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC, strengthening requirements for organizations that handle private user data. The updated regulations allow individuals to protect and control businesses' use of their personal information.
Who Has to Comply With the GDPR?
Your company has to comply with the GDPR if you process or handle personal data of individuals from the EU or EEA, even if you're based outside these areas. The law covers collection of personally identifiable information such as name, birthdate, Social Security number, and any other data points that could reveal an individual's identity.
The GDPR applies to your company if you sell products or services to users from these areas, and if you monitor their behavior when visiting your website. Although the GDPR applies to most types of organizations, some activities fall outside the scope of this law. Exceptions to the GDPR include data collection and storage for national security or law enforcement activities.
What Does the GDPR Require?
The GDRP requires you to meet its compliance standards if your company handles applicable user data. Your business must:
- Have a lawful reason to collect and use the information, such as legal or contractual obligation
- Be transparent about the purpose of data collection and use
- Obtain freely-given, informed consent from users
- Collect only the data you need for the specified purpose
- Implement and maintain strong security measures to protect user data from unauthorized access and use
- Give users a way to restrict, erase, and control their personal data
- Allow users to opt out of data collection and use
- Notify individuals and authorities of a data breach within 72 hours of learning about the breach
In addition, if your business uses the data in a way that poses a significant risk to individual privacy, you must conduct a data protection impact assessment. This process allows the company to identify and reduce the risks of their data collection activities.
How Can a Business Comply With the GDPR?
Your business can comply with the GDPR by fully understanding its requirements and taking the appropriate measures in response. If you collect data from EU or EEA residents or plan to do so, follow these steps to achieve GDPR compliance.
Conduct a Data Audit
First, document the scope of your organization's user data collection. Identify the types of information you collect, process and store from users. Next, determine the lawful basis to handle each type of data.
Where lawful basis exists, ensure you have valid user consent on file. If you don't have consent or lawful basis, you'll need to address those issues to comply with GDPR.
During the data audit, you should also flag and dispose of user data you no longer need. Minimizing the amount of user information you collect, store, and handle reduces the risk of an accidental data breach.
The auditing process helps you understand the entire organization's data collection and processing activities so you can take the appropriate steps toward GDPR compliance. It also creates a comprehensive document of these activities, which is a requirement for companies that have more than 250 employees and collect EU/EEA user data.
Perform a Data Protection Impact Assessment
A data protection impact assessment (DPIA) identifies data processing activities that pose a high risk to individual rights. Examples of potentially risky actions include:
- Collecting data for users younger than 18
- Using data to automate decisions about users that could have legal effects
- Processing personal data about a person's sexual orientation, gender, genetic data, religious beliefs, political opinions, race or ethnicity
- Gathering data through large-scale monitoring of a public place
- Tracking user behavior or location
- Using new technologies for data collection
The GDPR requires companies to conduct a DPIA when they engage in high-risk data collection activities. You must document the assessment process and take steps to reduce the established risks.
Review and Update Privacy Policies
Ensure your privacy notices and policies are transparent, easily accessible, and provide clear information. These notices should cover how and why your company processes personal data and identify the types of data you gather from website visitors.
Privacy notices should explain the individual's right to view and manage their data. You should also inform users about their right to consent to data collection and use.
Post your privacy policy in a prominent, accessible place that users can find and access quickly. The document should be concise and easy to understand, with clear identification of your business name and physical location. Notify your users about any updates you make to the privacy policy.
Obtain Valid Consent
GDPR compliance requires user consent for data collection and use. Review your existing consent process to make sure consent is:
- Unambiguous
- Informed
- Specific
- Freely given by the user
- Easy to withdraw
Plan to implement new consent protocols or update existing protocols to meet these GDPR standards. This example from Netflix explains that users can decide not to give consent or withdraw consent they previously provided. It also gives them a link where they can find out how to manage their personal data and consent settings:

Establish Data Security Measures
If you collect and store personal user data, your company is responsible for shielding this information from unauthorized disclosure, alteration, destruction, and use. Before you begin gathering this type of information, implement secure safeguards to prevent data breaches. Common data security strategies to incorporate include:
- Training employees at all levels in data security best practices
- Conducting regular security audits
- Establishing access controls such as firewalls and password protection
- Encrypting user data during storage and transmission
- Using two-factor authentication to strengthen user identification and prevent unauthorized access
- Limiting data access to the necessary personnel
- Removing identifiable information from user data
Give Users Access to Their Data
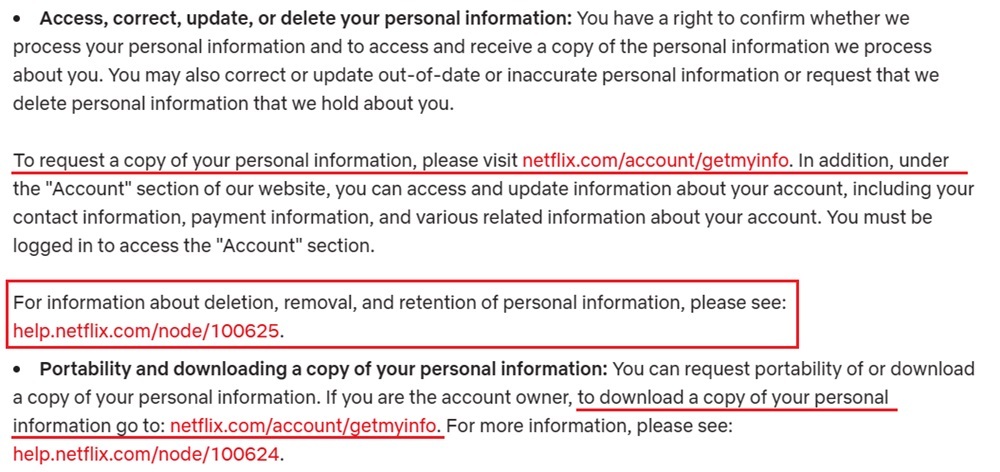
You'll need to provide users a way to access, view, download, and manage the data you've collected about them. The GDPR doesn't have specific requirements for how you fulfill this obligation, but suggests that you establish a process to respond to written data requests.
You'll see in the sample below that Netflix includes a URL where users can request, download, access, and update their personal information. The company's privacy policy also directs users to a second URL where they can learn how to retain, remove, and delete personal data collected by Netflix:
Prepare for a Possible Data Breach
Despite your best efforts to protect personal data, a breach could still impact user privacy and affect the reputation of your business. To prepare for this risk, develop and test procedures to detect, report, and respond to data security issues.
All team members should understand their responsibilities if a breach occurs. Have a clear plan to notify affected individuals and appropriate authorities about a data breach within 72 hours as mandated by GDPR.
Create Data Processing Agreements
If you use third-party service providers to process personal user data, have them sign processing agreements that establish clear expectations. Otherwise, you could be held responsible for non-compliant vendors. Many companies use third parties for data services such as:
- Encrypting email
- Monitoring and analyzing website traffic
- Collecting user data with online cookies
The data processing agreement should outline each party's data protection responsibilities to ensure GDPR compliance.
Continue Checking Compliance
GDPR compliance isn't a one-time activity, but an ongoing commitment to privacy protection. Your business should have a system for regular compliance audits. Periodically review data processing activities and update policies as needed to achieve ongoing GDPR compliance. Check your safeguards to ensure they remain effective and train new employees on current data handling procedures.
Assess these procedures frequently and update as needed so they continue to reflect evolving privacy laws. If you handle a significant volume of user data, consider creating a formal governance program or hiring an internal data compliance officer to own this process.
What Are the Penalties for GDPR Non-Compliance?
Enforcement authorities can order substantial fees and other penalties for failure to comply with GDPR. The law establishes two tiers of violations. Severe violations carry fines of up to 20 million Euros or 4% of your company's global revenue from the prior year (whichever is greater). Violations at this level directly impact a user's right to privacy and may include:
- Processing data without a lawful basis
- Collecting user information without consent
- Preventing individuals from viewing and managing their own data
- Transmitting user data without encryption
- Collecting prohibited types of data such as health information
Compliance failures without an immediate effect on privacy rights fall into the less-severe category. These violations result in fines of up to 10 million Euros or 2% of prior-year revenue.
As of April 2024, companies of all sizes have received more than 2,000 violations totaling more than $4.84 billion according to the GDPR Enforcement Tracker.
In several high-profile cases:
- TikTok received a fine of $372 million for transparency and data processing violations in 2023
- Amazon received an $887 million fine in 2021 for delivering targeted ads based on personal data without user consent
- Meta received a record-setting fine of $1.3 billion in 2023 for international transmission of user data without the appropriate protections
In addition to financial penalties, individuals affected by GDPR violations can seek financial compensation from your business.
Authorities may first issue a warning for minor violations. If you receive this type of notice, you typically have a specified amount of time to fix the issue before facing penalties. Read the communication carefully and take the appropriate steps to avoid significant fines.
Data privacy issues also impact your company's reputation. Beyond the official penalties, loss of trust in the business after a violation can reduce sales and affect your revenue.
Conclusion
Taking action to comply with the GDPR can shield your business from the significant cost of a violation. Strong, transparent data privacy policies and other safety measures demonstrate a commitment to protecting your users' individual rights. Start the process with a comprehensive audit to understand where your business stands in terms of GDPR and plan the necessary steps to achieve compliance. A proactive approach will also position you to adjust as needed to new data use regulations and changes to current laws.